Exploring Hyperbaric Oxygenation Therapy: Benefits, Risks, and the Science Behind It
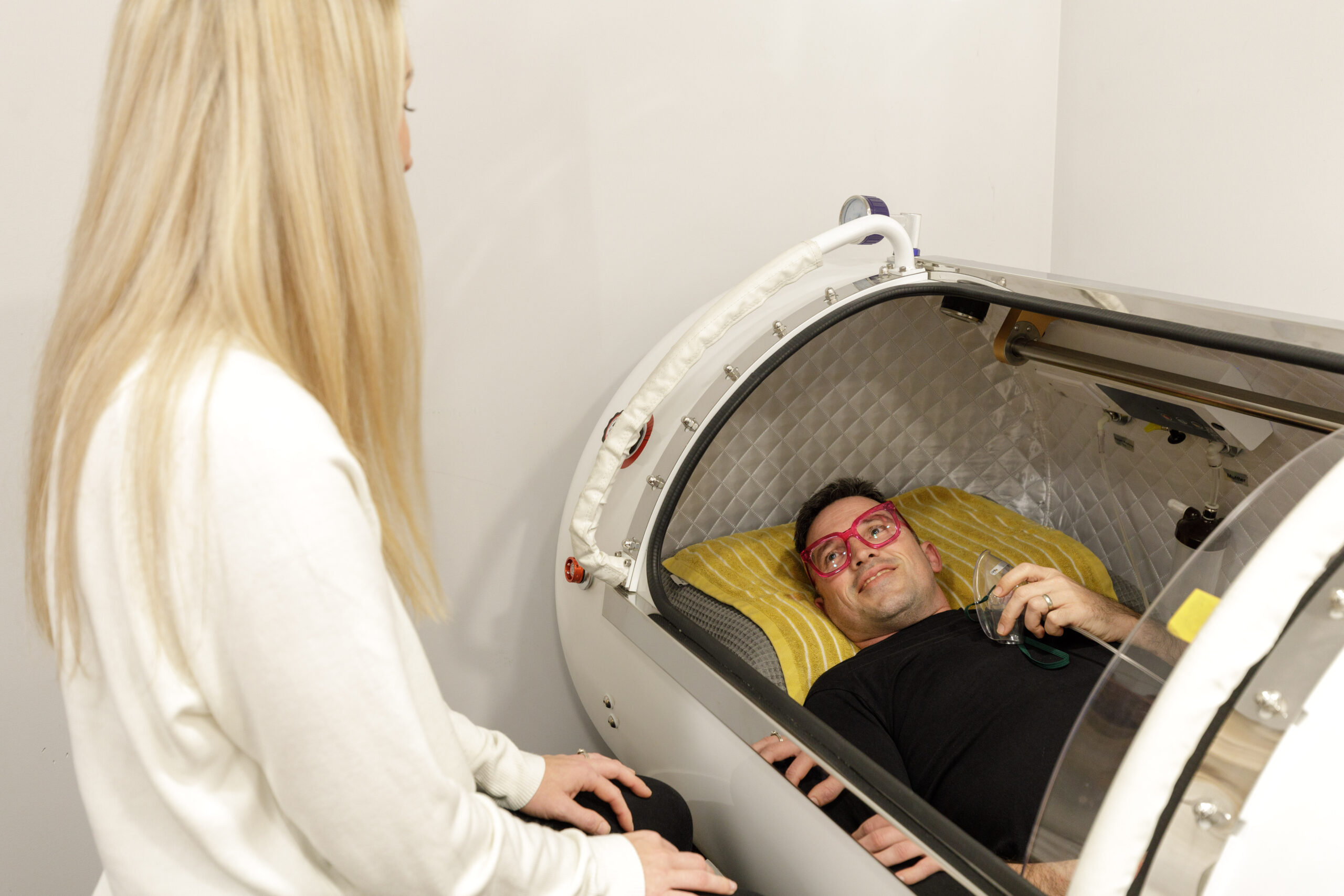
Hyperbaric Oxygenation Therapy (HBOT) is one of the most innovative and increasingly popular treatments in the medical field today. It involves breathing 100% oxygen in a pressurized chamber, and its uses range from treating chronic wounds to aiding recovery in athletes. As more people and medical professionals become aware of the potential benefits, HBOT is gaining traction as a therapy that could address a variety of conditions beyond its original use. But as with any medical treatment, it’s important to fully understand both the science behind it and the risks involved. This article explores the benefits, risks, and scientific foundation of hyperbaric oxygenation therapy.
What is Hyperbaric Oxygenation Therapy?
At its core, Hyperbaric Oxygenation Therapy involves breathing oxygen at higher-than-normal atmospheric pressure. Under normal circumstances, we breathe air with around 21% oxygen, and our blood is saturated with oxygen at atmospheric pressure. However, in an HBOT chamber, the pressure is increased—typically between 1.5 and 3 times normal atmospheric pressure—while patients breathe in 100% pure oxygen. This process allows oxygen to dissolve into the bloodstream more efficiently, allowing it to reach areas of the body that might have poor circulation or have been damaged due to injury or disease.
The therapy is usually administered in specially designed chambers, which can accommodate one or more patients. Some chambers are large enough to fit patients lying down, while others are designed for individual use.
The Science Behind Hyperbaric Oxygenation Therapy
The mechanism of HBOT is based on the fact that oxygen under pressure dissolves into blood plasma, allowing the oxygen to reach tissues that might not be receiving sufficient oxygen through the normal circulatory process. This includes areas with poor blood flow, damaged tissues, or those affected by certain medical conditions.
Increased oxygen levels stimulate several physiological processes, including:
- Enhanced Healing and Tissue Regeneration: The influx of oxygen accelerates the healing of wounds by promoting collagen production, a vital component in tissue repair.
- Angiogenesis: HBOT encourages the formation of new blood vessels, improving blood circulation in areas that might otherwise suffer from inadequate oxygen delivery. This is particularly important for healing damaged tissues and wounds.
- Reduced Inflammation: Increased oxygen levels can help modulate inflammatory responses, a crucial mechanism in healing, particularly for conditions that involve chronic inflammation.
- Increased White Blood Cell Activity: White blood cells are the body’s first line of defense against infection. The higher oxygen content helps these cells function more efficiently, enabling the body to fight off infections more effectively.
Medical Benefits of Hyperbaric Oxygenation Therapy
Over the years, a growing body of research has highlighted the therapeutic potential of HBOT in treating a wide range of medical conditions. These include:
1. Chronic Wounds and Non-Healing Ulcers
HBOT is often used to treat chronic wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers, which are difficult to heal due to poor circulation. The increased oxygen levels stimulate cell repair, improve tissue regeneration, and reduce the chances of infection. Studies have shown that HBOT can significantly accelerate healing in cases where traditional treatments have failed.
2. Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBI) and Stroke
Following brain trauma or a stroke, the brain tissue can suffer from a lack of oxygen, which can impede recovery. Hyperbaric oxygenation has been shown to improve the oxygenation of the brain, encouraging the repair and regeneration of brain cells. This therapy has been linked to improvements in cognitive function, memory, and motor skills in patients suffering from TBI and stroke.
3. Infections
HBOT has powerful antibacterial effects. It enhances the ability of white blood cells to fight infection and is particularly effective in treating certain infections, including those caused by anaerobic bacteria (bacteria that thrive in low-oxygen environments). For example, infections like osteomyelitis (bone infection) and gangrene, which can be difficult to treat with antibiotics alone, have shown improvement with HBOT.
4. Burns and Radiation Injuries
For burn victims, HBOT can significantly accelerate the healing process, reducing the extent of scarring and promoting faster tissue recovery. Similarly, patients undergoing radiation therapy for cancer treatment often experience damage to healthy tissues, which can be mitigated with HBOT. The therapy aids in the healing of tissues affected by radiation burns and enhances recovery.
5. Sports Injuries
Athletes frequently use HBOT to aid in the recovery of soft tissue injuries like strains, sprains, and ligament tears. The increased oxygen delivery helps to heal tissues more quickly, reduces swelling, and reduces recovery time between intense athletic activities. Many athletes swear by its ability to get them back to peak performance faster.
6. Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Emerging research suggests that HBOT could potentially improve cognitive health in conditions like Alzheimer’s and even mild cognitive impairments. The theory is that the increased oxygen levels may help in reducing the neurodegenerative damage in the brain and stimulate the regeneration of damaged neurons. However, more research is needed to confirm these findings conclusively.
Risks and Side Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygenation Therapy
Like any medical treatment, HBOT is not without its risks. While side effects are generally rare and mild, there are some concerns and contraindications to consider before undergoing therapy.
1. Barotrauma
One of the most common risks associated with HBOT is barotrauma, which refers to pressure-related injuries, typically to the ears or sinuses. This occurs because the increased pressure can cause discomfort or damage to areas of the body that are sensitive to changes in pressure. Patients are often advised to equalize the pressure in their ears (similar to what’s done when diving) to avoid this.
2. Oxygen Toxicity
Breathing 100% oxygen for extended periods can lead to oxygen toxicity, which can damage the lungs and central nervous system. Symptoms of oxygen toxicity include dizziness, nausea, seizures, and lung irritation. However, modern hyperbaric chambers are carefully monitored to ensure that patients do not exceed safe oxygen exposure levels, reducing the risk of this issue.
3. Fire Hazard
The use of pure oxygen presents a fire risk, and this is why hyperbaric chambers are equipped with strict fire safety protocols. Oxygen is highly flammable, and it’s essential for patients to remove any items such as flammable clothing, oils, or lotions before entering the chamber. Chambers are also constructed to prevent ignition from any sources of heat.
4. Claustrophobia
Some individuals may feel anxiety or claustrophobia when confined to the relatively small space of a hyperbaric chamber. While chambers have windows and are well-ventilated, patients who experience significant discomfort or panic attacks may find the experience stressful.
Is HBOT Right for You?
While hyperbaric oxygenation therapy offers many potential benefits, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider before undergoing treatment. Each individual’s medical history and specific condition should be considered to determine if HBOT is an appropriate option. In some cases, the risks may outweigh the benefits, particularly if a patient has certain underlying conditions such as lung disease, heart disease, or epilepsy.
Conclusion
Hyperbaric Oxygenation Therapy has emerged as a powerful medical tool with a wide array of potential applications, ranging from wound healing to brain injury recovery. The therapy’s ability to accelerate the body’s natural healing processes by delivering increased oxygen to tissues can lead to remarkable improvements in a variety of medical conditions. However, as with any treatment, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks, including barotrauma, oxygen toxicity, and claustrophobia, and to consult with a healthcare provider to ensure it’s the right option. As research continues, the full range of HBOT’s benefits will likely expand, offering new hope for individuals with a variety of challenging health conditions.